Pak. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010; 43(2): 105-108
Exposure to illuminated salt lamp increases 5-HT metabolism: A serotonergic perspective to its beneficial effects
Hajra Naz* and Darakhshan J Haleem
Neurochemistry and Biochemical Neuropharmacology Research Unit, Department of Biochemistry, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan
Abstract: For centuries people have known the ability of salt rock crystal to improve air qualities by enriching it with negative ions. Salt lamps are thought to be a good source of negative ions. In view of the claim of the salt lamp sellers regarding its beneficial effects the neurochemical study was an extension of the behavioral study conducted in rats. Test animals were exposed to salt lamp for 14 weeks. Decapitation after 14 weeks, followed by neurochemical analysis showed that brain tryptophan and 5-HT metabolism were increased after salt lamp exposure. The results are discussed in relevance to its antidepressant effects and other behavioral activities monitored previously. Keywords: Illuminated salt lamp, 5-HT metabolism, brain tryptophan, serotonin.
Received: January 12, 2010 Accepted: April 27, 2010 *Author Correspondence: Hajra20052005@yahoo.com
INTRODUCTION
Previous studies have shown that exposure to salt lamp enhances memory, lessens anxiety and improves activity in animal models. The sellers of salt lamp claim that the negative ions produced from salt lamp (which is one of its proposed mechanism) could be recommended for their beneficial effects in enhancing immunity, increased alertness, increased work productivity, increased lung capacity, and reduced susceptibility to colds and flu. The present study was designed to investigate the serotonergic mechanisms involved in the previously published data.
It is a common observation that people develop feelings of pleasantness and well-being after storm, when the environment is clean and fresh; filled with abundant negative ions. Studies have shown that novel purification systems using positively and negatively charged ions were developed to create comfortable living environments. A balance of negative and positive ions is essential for healthy living. Various natural and environmental factors such as hot and dry winds, pollution, TV screens and many other human activities produce positive ions which create an imbalance of these ions. Salt crystal lamps have properties, enhancing on health and well-being. It is said that they emit ions. The negative ions are generated by a continuous interplay of water attraction and evaporation. The salt crystal lamp attracts water molecules from the surrounding air to its warm surface. The water and salt form a solution. In the process of evaporation of the solution, due to the heat of the lamp, negatively charged ions are created. Both positive and negative ions are created but much more negative ions than positive ions are created, therefore providing a surplus of negative ions. Natrium is positively charged. This unique ion emission interplay ability with water is because of salts neutral atomic structure.
Scientific research clearly points out that a balanced ratio between negative and positive ions in the air we breathe affects our well-being. From this study warm Salt Crystal lamps can be seen to be the natural ion generators. The efficacy of negative ions has been also well-proven from previous and current research mentioned below. Negative ions exert bactericidal effects on staphylococcus albus. Hydrated negative ions emitted from air-cleaning devices such as plasma generators have also known to produce bactericidal effects. Biocidal effects have also been demonstrated by Marin and his coworkers on gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Treatment with negative ions has shown remarkable diminution in the allergen against Japanese cedar pollen allergies 2. Studies have been also focusing on health benefits of speleotherapy for chronic congestive problems in salt mines. Studies conducted in Russia have demonstrated speleotherapy courses noticeably diminish broncho-obstructive syndrome and improved ventilation of pediatric asthmatics . Courses of speleotherapy in the microclimatic conditions of salt mines have shown to increase the number and functional activity of T-lymphocytes, while normalization of B-lymphocytes resulting in alleviating bronchial asthma attacks. Equally important as the ionizing effect, is the Salt crystal lamps’ ability to neutralize and purify air. Depending on the size and the surface area of Salt Crystal lamp the purification of surrounding air takes place during the transformation cycle in water attraction and evaporation, involving hydrogen and oxygen, as well as sodium and chloride, resulting in significant purification of air. This property will greatly benefit asthma and allergy sufferers. Apart from the natural ionization Naz and Haleem of salt lamps, it could also harmonize and enhance our system and functions by electromagnetic radiations and color therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The experiment was conducted on 24 male rats. The animals were randomly divided into controls and salt lamp exposed group. Animals assigned to experimental group were exposed to 8 salt amps purchased from Java food International, Clifton, Karachi, Pakistan, were kept in a small room (10x8x10) ft. The lamps were left on for 24 h for a period of 14 weeks. Lamp bulbs were replaced immediately if they were fused so as to ensure that the rats were exposed uninterruptedly to the illuminated lamps. Their counter parts were also housed individually and placed in a room devoid of salt lamps so as to provide them with a normal environment. The animals were decapitated after the 14th week by cervical dislocation plasma and brains were stored at -70°C for eurochemical analysis. The ethical conditions were maintained throughout the experiment.
Removal of brain from cranial cavity
After decapitation the skin was cut with the help of scissors. A long incision was made with the help of scissors and the two halves of the skull were separated. The connections were loosened and he brain was taken out from the cranial cavity and placed on the glass plate.
Extraction of TRP from plasma
To 0.01 ml of plasma, 0.2 ml of 0.4M perchlorate containing 0.1% sodium metabisulphate, 0.01% EDTA and 0.1% cystine was added and thoroughly mixed. The mixture was then centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 10-15 min at 4o C in Eppendorf tubes. Supernatants were then used for determination of TRP by HPLC.
HPLC-EC determination of tryptophan, 5-HT and 5-HIAA
Tryptophan, 5-HT and 5-HIAA from brain samples were extracted as described previously. A 5µ ODS separation column 4.0 mm and 250 mm length was used. Mobile phase comprised methanol (14%), octyl sulphate (0.023 %) and EDTA (.0035%) in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 2.9 was passed through the column at an operating pressure of 2000-3000 psi with the help of Waters 510 HPLC pump. Electrochemical detection was achieved on Shimadzu- L –EC 6A detector at an operating potential of 0.8 V. Tryptophan was detected in a separate run at an operating potential of 1.0 V.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 1 shows the effects of salt lamp exposure on plasma TRP (a) and brain TRP (b) in rats. Data analysed by t test showed increases in plasma TRP (a) (P<0.05) and brain TRP (b) (P<0.05). Figure 2 shows the effects of salt lamp exposure on brain 5-HT (a), brain 5-HIAA (b) and turn over ratio (c) in rats. Data analyzed by t-test showed decreases in 5-HT (P<0.05), increases in 5- HIAA (P<0.05) and a significant turn over ratio (P<0.01).
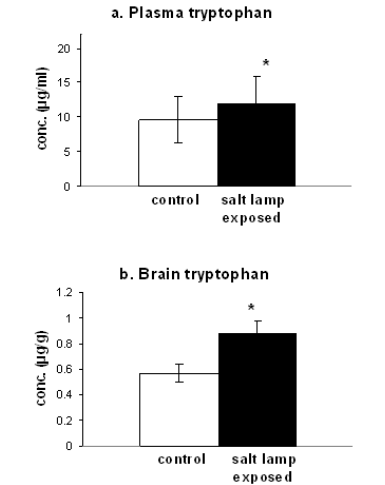
Figure 1: Effects of salt lamp exposure (14 weeks) on plasma tryptophan (a) and brain tryptophan (b).
Previous studies have demonstrated that serotonin plays a pivotal role in the modulation of anxiety and depression related traits, as well as in the pathogenesis of anxiety related disorders and depression. Many studies converge to a point that increasing 5-HT function is antidepressant. Our results demonstrate that 5-HT metabolism was increased in animals exposed to salt amp (Figure 2 2). The above findings could thus suggest that exposure to salt lamp could be used to relief depressive symptomatology. Animals exposed to salt lamp exhibited increased plasma RP (Figure 5-HT metabolism and salt lamp 1a) concentrations which could have increased due to a decrease in TRP pyrrolase activity, thus providing a greater availability of TRP to the brain as seen in the present study (Figure 1b).
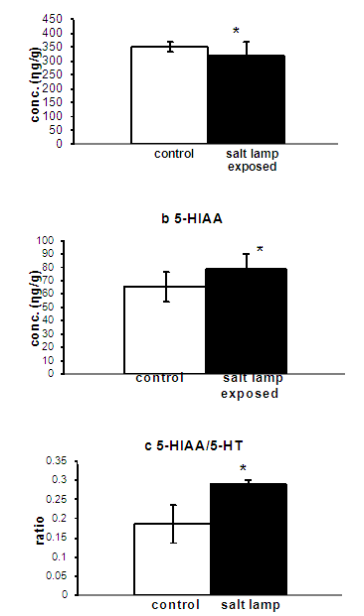
Figure 2: Effects of salt lamp exposure (14 weeks) on brain 5-HT (a), brain 5-HIAA (b) and turnover ratio (c).
TRP being the precursor of 5-HT, can modulate the synthesis of 5-HT as the enzyme TRP hydroxylase which is confined to the serotonergic neurons and catalyzes the rate limiting step of 5-HT synthesis is not saturated with the substrate at normal brain TRP concentrations. Thus an increase in TRP concentration in the plasma could have increased the competition of TRP with other large neutral amino acids; hence increased uptake of TRP by the serotonergic neurons resulting in increased 5-HT synthesis. However in the present study 5-HT synthesis decreased, although plasma and brain TRP concentrations increased in rats exposed to salt lamp. These decreases of 5-HT could be explained in terms of increased 5-HT metabolism as evident from increased 5-HIAA (Figure 2b) concentrations and increased turnover ratio (Figure 2c). Thus the present study suggests that enhanced degradation of 5-HT by monoamine oxidases could have occurred in animals exposed to salt lamp depending upon its concentration in the plasma and brain. Increased 5-HT metabolism is suggested to improve cognitive performance where as decreasing 5-HT levels have shown to impair cognition. Haider and co-workers from our laboratory have demonstrated that long term TRP administration enhances cognitive performance and increases 5-HT metabolism. Our results compliment the previously published data reporting improved memory as assessed in RAM. Enhanced cognitive performance in rats could be due to increased TRP availability to the rain and increased 5-HT metabolism as observed in the previously published study. Increased activity of animals was observed in animals exposed to salt lamp. Increased in activity is difficult to explain in terms increased 5-HT metabolism because increasing 5-H T decreases activity. It is possible that increased activity might have occurred via another mechanism. One possible explanation could be on the basis of serotonergic Dopaminergic interaction of neurons at the level of caudate to control motor activity. 5-HT acts via 5-HT-2C receptors on the DA neurons to decrease motor activity. Stimulation of somatodendritic 5-HT receptors by enhanced 5- HT turnover in raphe region could decrease the availability of 5-HT in the caudate, releasing DA neurons from the inhibitory effects of 5-HT and elicit hyperactivity. It is therefore possible that exposure of animals to salt lamp largely increases brain 5-HT metabolism (5-HT metabolism increased in whole brain) in the somatodendritic region to decrease the availability of 5-HT at DA neurons and elicit improved activity. The present study also shows a fearless response of the animals to the novel environment of the light/ dark box and height plus openness of the elevated plus maze thus helping us to suggest that salt lamp exposure might produce anxiolytic effect. The anxiolytic effects however cannot be explained on the basis of increasing 5-HT metabolism as observed in the present study because decreasing 5-HT functions are anxiolytic. It is possible that alt lamp elicits a fearless response in the above experiments via some other mechanism.
Naz and Haleem
We suggest that usage of salt lamp might be helpful environmental tool to relieve anxiety, improve memory. Its anti-depressant effects could be secondarily responsible to improve activity in the activity box. Figure 3 shows a proposed mechanism of action of the beneficial effects of salt lamp environment.
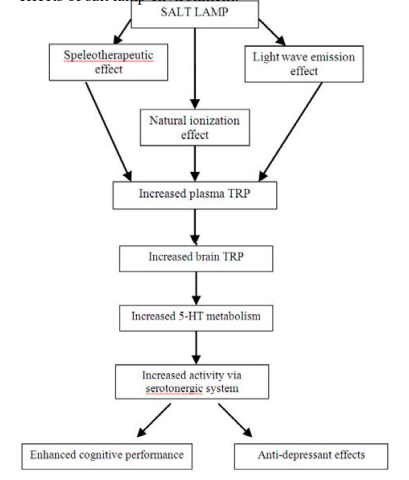
Figure 3: Proposed mechanism of action of the beneficial effects of salt lamp environment.


 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά



